Publications
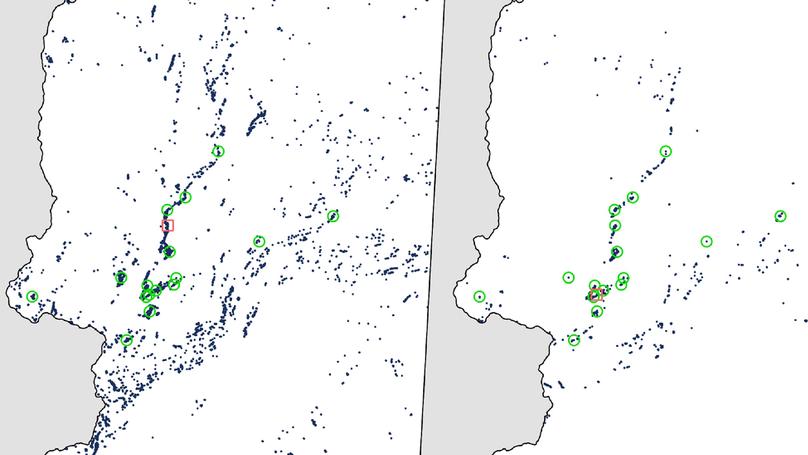
This study addresses imbalanced data challenges in Mineral Prospectivity Mapping (MPM) using geophysical data from Lapland, Finland. It applies data-level imbalanced handling techniques and algorithm-level threshold adjustments to improve model predictions of rare mineral deposits. The performance of four ML models—MLP, RF, DT, and LR—was evaluated. The MLP model achieved the best accuracy (97.13%) on balanced data using synthetic oversampling.
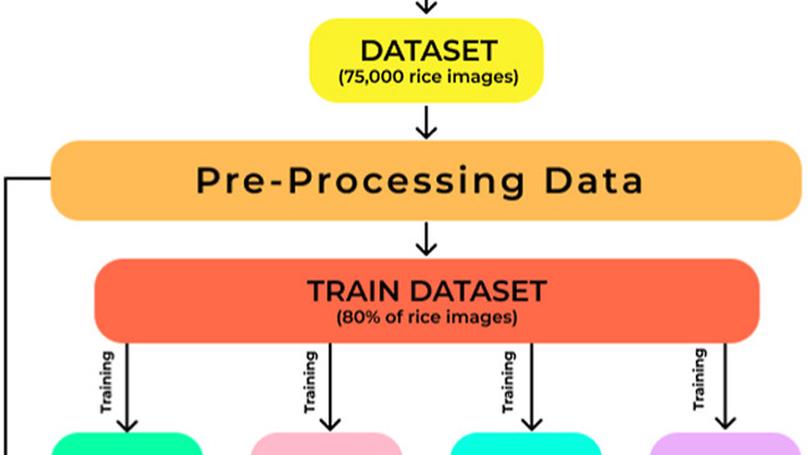
This study explores deep-learning models for automated rice grain classification, which is essential for quality control, cost optimization, and supply chain efficiency. Testing models like ResNet, VGG, EfficientNet, and MobileNet on a dataset of 75,000 images across five rice categories, results showed that EfficientNet achieved the highest accuracy (99.67%), while MobileNet excelled in speed. The study concludes that deep-learning models offer scalable, efficient handling of large, complex data, outperforming traditional machine-learning methods.
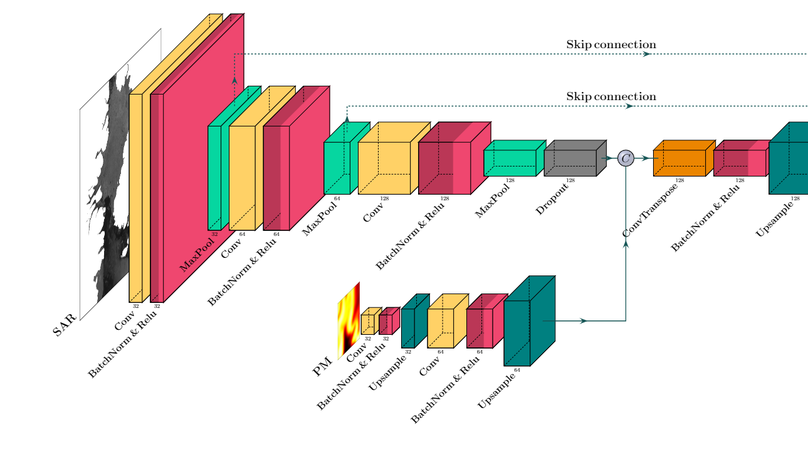
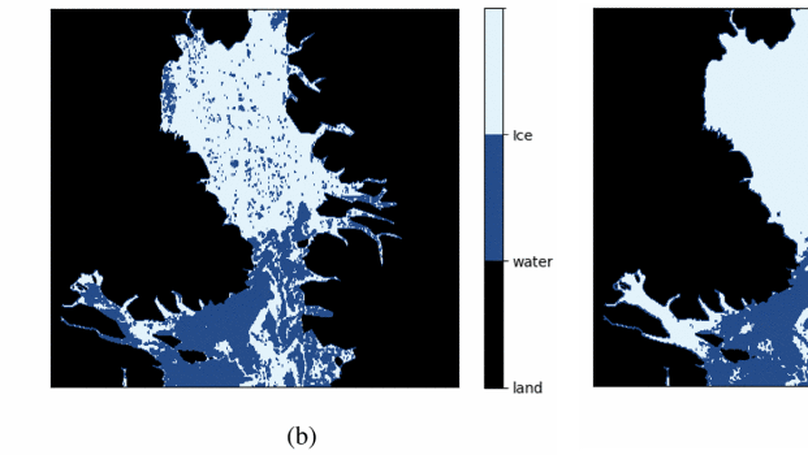
This paper presents a new method using a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to estimate sea ice concentration in the Baltic Sea by combining Sentinel-1 and AMSR2 data. The CNN architecture retains different resolution inputs without losing valuable information. By using a focal loss function and skip connection, the proposed model achieves a high R2 score of 90.6%.
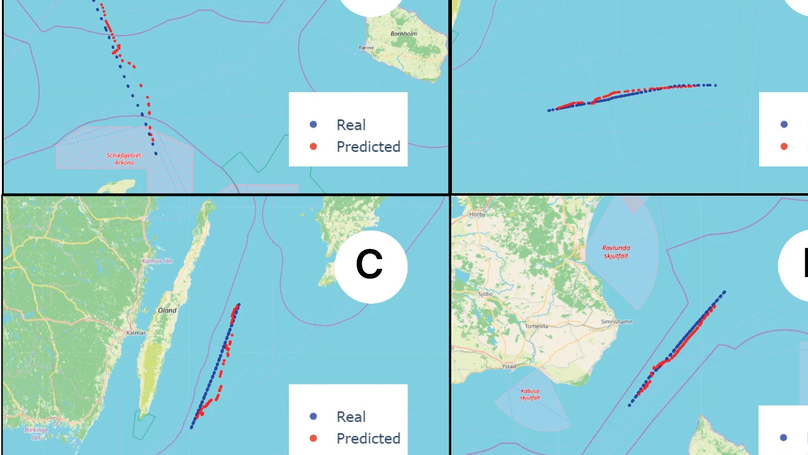
This study introduces short-term and long-term vessel trajectory prediction methods to enhance maritime traffic management. Tested with Baltic Sea AIS data, the short-term method shows high accuracy, while the long-term method optimizes speed and memory, promising improvements in efficiency and safety.
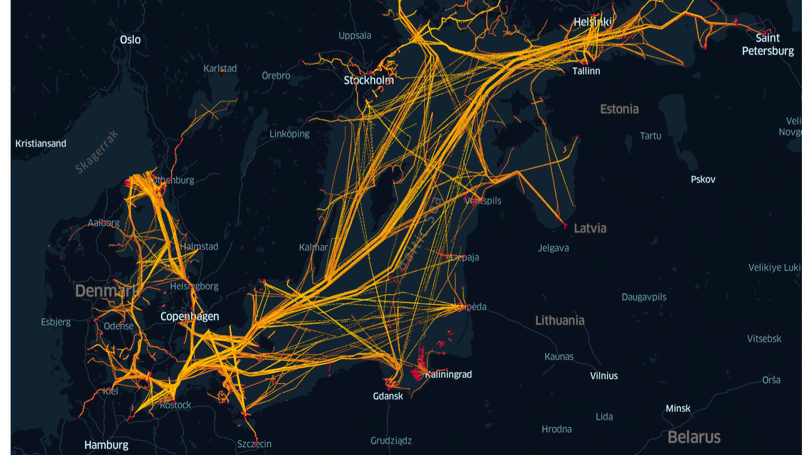
The paper explores different clustering methods using AIS data to detect two dangerous abnormal behaviors in maritime vessels like dark ships (vessels turning off AIS for illegal activities) and spiral vessel movements. It evaluates K-means, DBSCAN, AP, and GMM techniques using three months of AIS data from the Baltic Sea. Results show that K-means is effective in identifying these threatening events, contributing to improving maritime safety.
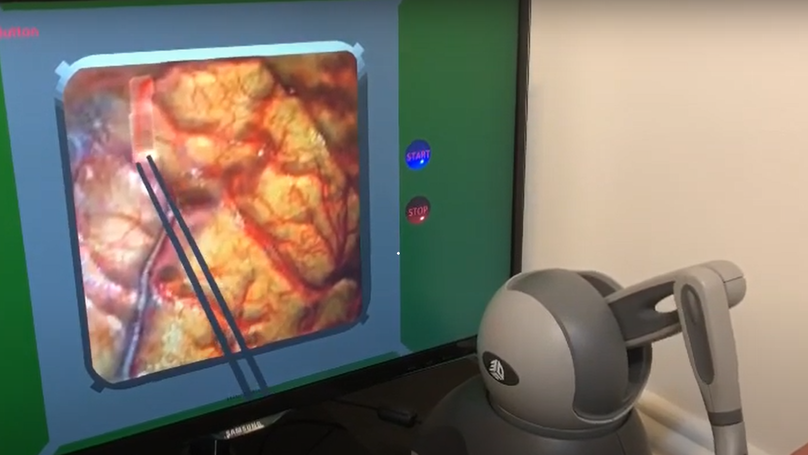
In recent years, one of the most widely used tools in the training and evaluation of physicians and surgeons is surgical simulators. Introducing virtual reality and adding haptic technology to the field has made it feasible to develop ever-better surgical simulators. In this regard, we set out to design a brain surgery bipolar electrocoagulation simulator using haptic technology.